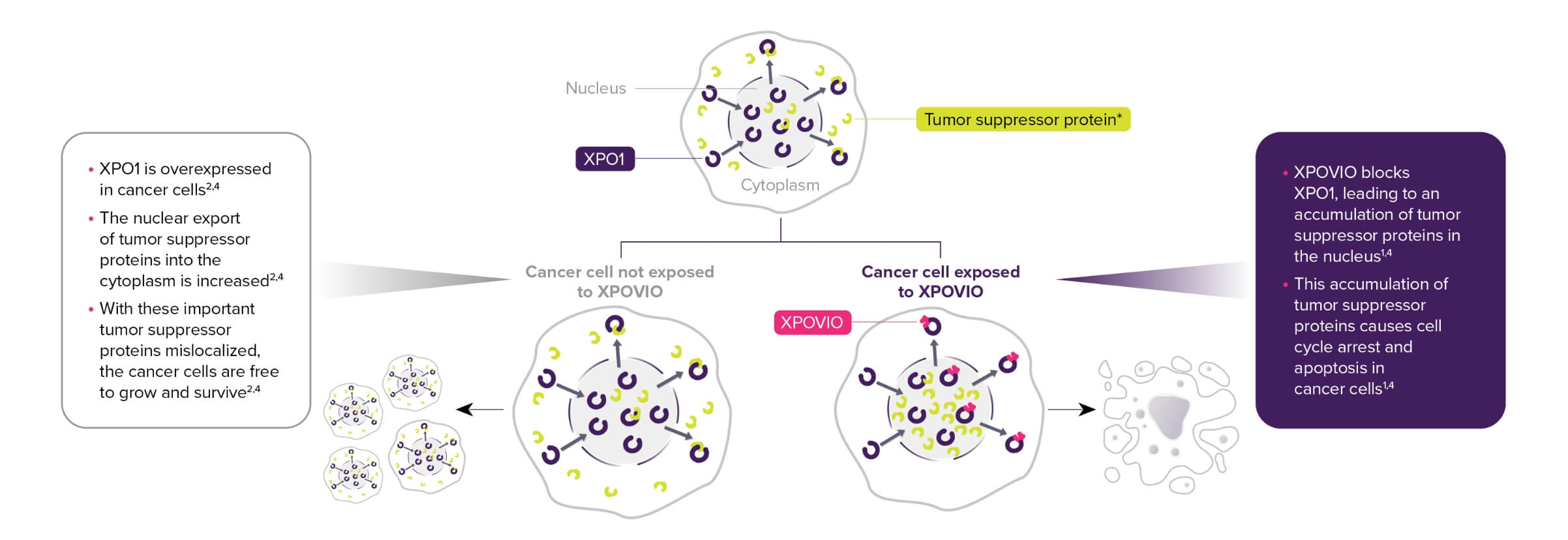
Thrombocytopenia: XPOVIO can cause life-threatening thrombocytopenia, potentially leading to hemorrhage. Thrombocytopenia was reported in patients with multiple myeloma.
Thrombocytopenia is the leading cause of dosage modifications. Monitor platelet counts at baseline and throughout treatment. Monitor more frequently during the first 3 months of treatment. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of bleeding. Interrupt, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction.
Neutropenia: XPOVIO can cause life-threatening neutropenia, potentially increasing the risk of infection.
Monitor more frequently during the first 3 months of treatment. Consider supportive measures, including antimicrobials and growth factors (e.g., G-CSF). Interrupt, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction.
Gastrointestinal Toxicity: XPOVIO can cause severe gastrointestinal toxicities in patients.
Nausea/Vomiting/Diarrhea: Provide prophylactic antiemetics or treatment as needed.
Anorexia/Weight Loss: Monitor weight, nutritional status, and volume status at baseline and throughout treatment and provide nutritional support, fluids, and electrolyte repletion as clinically indicated.
Hyponatremia: XPOVIO can cause severe or life-threatening hyponatremia.
Monitor sodium level at baseline and throughout treatment.
Serious Infection: XPOVIO can cause serious and fatal infections. Atypical infections reported after taking XPOVIO include, but are not limited to, fungal pneumonia and herpesvirus infection.
Neurological Toxicity: XPOVIO can cause life-threatening neurological toxicities.
Coadministration of XPOVIO with other products that cause dizziness or mental status changes may increase the risk of neurological toxicity.
Advise patients to refrain from driving and engaging in hazardous occupations or activities, until the neurological toxicity fully resolves. Institute fall precautions as appropriate.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: XPOVIO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential and males with a female partner of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with XPOVIO and for 1 week after the last dose.
Cataracts: New onset or exacerbation of cataract has occurred during treatment with XPOVIO. The incidence of new onset or worsening cataract requiring clinical intervention was reported.
The most common adverse reactions (ARs) (≥20%) in patients with multiple myeloma who received XVd were fatigue, nausea, decreased appetite, diarrhea, peripheral neuropathy, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased weight, cataract, and vomiting.
Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities (≥10%) were thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, hypophosphatemia, anemia, hyponatremia and neutropenia.
Fatal ARs occurred in 6% of patients within 30 days of last treatment. Serious ARs occurred in 52% of patients. Treatment discontinuation rate due to ARs was 19%. The most frequent ARs requiring permanent discontinuation in >2% of patients included fatigue, nausea, thrombocytopenia, decreased appetite, peripheral neuropathy and vomiting. Adverse reactions led to XPOVIO dose interruption in 83% of patients and dose reduction in 64% of patients.
No overall difference in effectiveness of XPOVIO was observed in patients >65 years old when compared with younger patients. Patients ≥65 years old had a higher incidence of discontinuation due to an adverse reaction (AR) and a higher incidence of serious ARs than younger patients.
The effect of end-stage renal disease (CLCR <15 mL/min) or hemodialysis on XPOVIO pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc. at 1-888-209-9326 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
© 2023 Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc.