This site is intended for US healthcare professionals only.
- Prescribing Information
Xd part 2 clinical trial: a multicenter, single-arm, open-label study of adult patients with RRMM1
(N=122)
Adult patients with RRMM who had received 3 or more prior anti-MM regimens
Xd
Patients received 80 mg orally in combination with 20 mg dexamethasone on days 1 and 3 of every week
Prespecified subgroup analysis
- The approval of XPOVIO + dexamethasone was based on its efficacy and safety in 83 adult patients whose disease was refractory to bortezomib, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, pomalidomide, and daratumumab1
- The benefit-risk ratio appeared to be greater in this more heavily pretreated population than in the overall trial population1
Primary endpoint
- Overall response based on IMWG Uniform Response Criteria for Multiple Myeloma1,3
Select patient characteristics
Baseline patient demographics1
N=83
Median age
65 years (range, 40-86)
Age ≥75 years
15%
Male
61%
Female
39%
Median years from diagnosis to start of study treatment
7 (range, 1-23)
Median prior treatment regimens*
8 (range, 4-18)
≥8 prior treatment regimens4
54.2%
*Treatment regimen = line of therapy.
The clinical trial included patients who had high-risk cytogenetics and rapidly progressing disease1
100%
of patients (N=83) were refractory to1
- Lenalidomide
- Pomalidomide
- Bortezomib
- Carfilzomib
- Daratumumab
57%
of patients (N=83) in the subgroup5
Includes any of the following:
- del(17p)/p53
- t(14;16)
- t(4;14)
- 1q21
22%
median increase in disease burden5 between screening and first day of therapy (n=107)
84% of patients enrolled had received a prior stem cell transplant5

The Xd trial results demonstrated significant responses in adult patients with RRMM whose disease was refractory to bortezomib, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, pomalidomide, and daratumumab (N=83)1

1
patient demonstrated sCR
0
patients demonstrated a CR
4
patients demonstrated VGPR
16
patients demonstrated PR
Rapid and durable response with Xd
Patients responded to Xd within a median of 4 weeks1


Median time to first response (range, 1-10 weeks)




Median DOR (95% Cl, 2.3-not estimable)
Patients stayed on Xd treatment for a median of 8 weeks (range, 1-60 weeks)1
ARs with XPOVIO 80 mg + dexamethasone 20 mg administered twice weekly1
ARs
(≥10%)
(≥10%)
Any Grade (N=202) (%)
Grade ≥3 (N=202) (%)
Thrombocytopeniaa
74
61
Fatigueb
73
22
Nausea
72
9
Anemiac
59
40
Decreased appetite
53
4.5
Weight decreased
47
0.5
Diarrhea
44
6
Vomiting
41
3.5
Hyponatremia
39
22
Neutropeniad
34
21
Leukopenia
28
11
Constipation
25
1.5
Dyspneae
24
3.5k
Upper respiratory tract infectionf
21
3
Coughg
16
0
ARs
(≥10%) (continued)
(≥10%) (continued)
Any Grade (N=202) (%)
Grade ≥3 (N=202) (%)
Mental status changesh
16
7
Pyrexia
16
0.5
Hyperglycemia
15
7
Dizziness
15
0
Insomnia
15
2
Lymphopenia
15
10
Dehydration
14
3.5
Hypercreatininemiai
14
2
Pneumoniaj
13
9k
Epistaxis
12
0.5
Hypokalemia
12
3.5
Dysgeusia
11
0
Vision blurred
10
0.5
Headache
10
0
aThrombocytopenia includes thrombocytopenia and platelet count decreased.
bFatigue includes fatigue and asthenia.
cAnemia includes anemia and hematocrit decreased.
dNeutropenia includes neutropenia and neutrophil count decreased.
eDyspnea includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional, and dyspnea at rest.
fUpper respiratory tract infection includes upper respiratory tract infection, respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, nasopharyngitis, bronchitis, bronchiolitis, respiratory syncytial virus infection, parainfluenza virus infection, rhinitis, rhinovirus infection, and adenovirus infection.
gCough includes cough, productive cough, and upper-airway cough syndrome.
hMental status changes includes mental status changes, confusional state, and delirium.
iHypercreatininemia includes hypercreatininemia and hypercreatinemia.
jPneumonia includes pneumonia, atypical pneumonia, lung infection, lower respiratory tract infection, pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, pneumonia aspiration, pneumonia influenzal, and pneumonia viral.
kIncludes fatal event.
-
The treatment discontinuation rate due to ARs was 27%
- Reduction or interruption of XPOVIO dose occurred in 53% and 65% of patients, respectively
- The most frequent ARs requiring permanent discontinuation in ≥4% of patients included fatigue, nausea, and thrombocytopenia
- The rate of fatal ARs was 9%
Recommended Monitoring for Safety1
-
Monitor at baseline and during treatment as clinically indicated:
- Complete blood count with differential
- Standard blood chemistry
- Body weight
- Nutritional status
- Volume status
- Monitor more frequently during the first 3 months of treatment
Recommended Concomitant Treatments1
- Advise patients to maintain adequate fluid and caloric intake throughout treatment
- Consider intravenous hydration for patients at risk of dehydration
- Provide prophylactic concomitant treatment with a 5-HT3 antagonist and/or other antinausea agents prior to and during treatment with XPOVIO
Xd dosing schedule for RRMM1
The recommended dosage for RRMM patients on XPOVIO is 80 mg (four 20-mg tablets) taken with dexamethasone 20 mg.

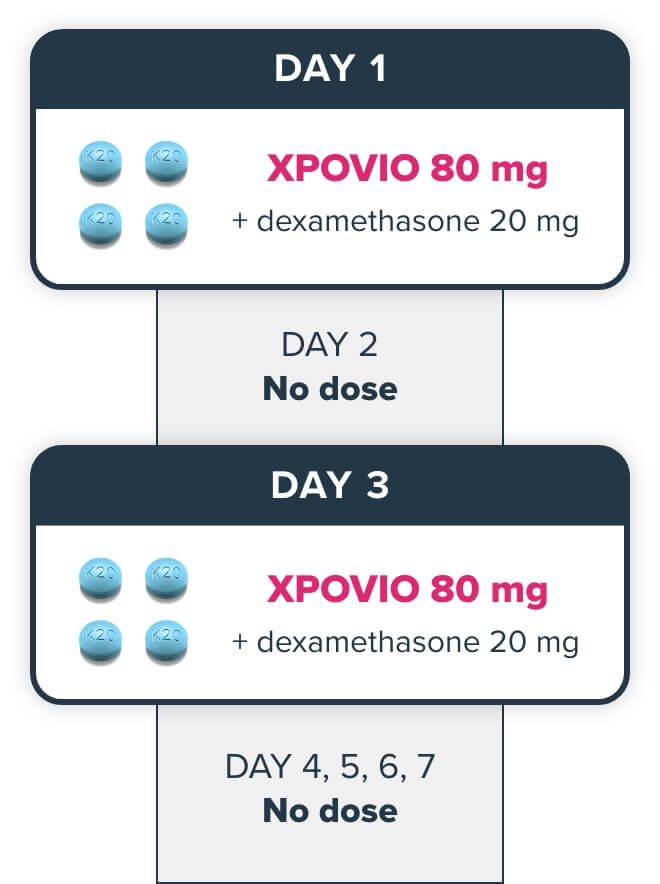

= 20 mg
Patients should take 2 prophylactic antiemetics, including a 5-HT3 antagonist. See antiemetics.
For additional information regarding the administration of dexamethasone, refer to its prescribing information.

Download the Dosing and Dosage Modification Guide for Xd
DownloadAbbreviations: AR, adverse reaction; CR, complete response; DOR, duration of response; IMWG, International Myeloma Working Group; MM, multiple myeloma; ORR, overall response rate; PR, partial response; RRMM, relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma; sCR, stringent complete response; VGPR, very good partial response; Xd, selinexor and dexamethasone.
References: 1. XPOVIO (selinexor) [prescribing information]. Newton, MA. Karyopharm Therapeutics, Inc. 2. Palumbo A, Rajkumar SV, San Miguel JF, et al. International Myeloma Working Group consensus statement for the management, treatment, and supportive care of patients with myeloma not eligible for standard autologous stem-cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(6):587-600. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.48.7934 3. Kumar S, Paiva B, Anderson KC, et al. International Myeloma Working Group consensus criteria for response and minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(8):e328-e346. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30206-6 4. Data on file. Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc. 2022. 5. Chari A, Vogl DT, Gavriatopoulou M, et al. Oral selinexor-dexamethasone for triple-class refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(8):727-738. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1903455
INDICATION
XPOVIO® (selinexor) is a prescription medicine approved in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone (XVd) to treat adult patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least one prior therapy.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Thrombocytopenia: XPOVIO can cause life-threatening thrombocytopenia, potentially leading to hemorrhage. Thrombocytopenia was reported in patients with multiple myeloma.
Thrombocytopenia is the leading cause of dosage modifications. Monitor platelet counts at baseline and throughout treatment. Monitor more frequently during the first 3 months of treatment. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of bleeding. Interrupt, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction.
Neutropenia: XPOVIO can cause life-threatening neutropenia, potentially increasing the risk of infection.
Monitor more frequently during the first 3 months of treatment. Consider supportive measures, including antimicrobials and growth factors (e.g., G-CSF). Interrupt, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction.
Gastrointestinal Toxicity: XPOVIO can cause severe gastrointestinal toxicities in patients.
Nausea/Vomiting/Diarrhea: Provide prophylactic antiemetics or treatment as needed.
Anorexia/Weight Loss: Monitor weight, nutritional status, and volume status at baseline and throughout treatment and provide nutritional support, fluids, and electrolyte repletion as clinically indicated.
Hyponatremia: XPOVIO can cause severe or life-threatening hyponatremia.
Monitor sodium level at baseline and throughout treatment.
Serious Infection: XPOVIO can cause serious and fatal infections. Atypical infections reported after taking XPOVIO include, but are not limited to, fungal pneumonia and herpesvirus infection.
Neurological Toxicity: XPOVIO can cause life-threatening neurological toxicities.
Coadministration of XPOVIO with other products that cause dizziness or mental status changes may increase the risk of neurological toxicity.
Advise patients to refrain from driving and engaging in hazardous occupations or activities, until the neurological toxicity fully resolves. Institute fall precautions as appropriate.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: XPOVIO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential and males with a female partner of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with XPOVIO and for 1 week after the last dose.
Cataracts: New onset or exacerbation of cataract has occurred during treatment with XPOVIO. The incidence of new onset or worsening cataract requiring clinical intervention was reported.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (ARs) (≥20%) in patients with multiple myeloma who received XVd were fatigue, nausea, decreased appetite, diarrhea, peripheral neuropathy, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased weight, cataract, and vomiting.
Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities (≥10%) were thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, hypophosphatemia, anemia, hyponatremia and neutropenia.
Fatal ARs occurred in 6% of patients within 30 days of last treatment. Serious ARs occurred in 52% of patients. Treatment discontinuation rate due to ARs was 19%. The most frequent ARs requiring permanent discontinuation in >2% of patients included fatigue, nausea, thrombocytopenia, decreased appetite, peripheral neuropathy and vomiting. Adverse reactions led to XPOVIO dose interruption in 83% of patients and dose reduction in 64% of patients.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
No overall difference in effectiveness of XPOVIO was observed in patients >65 years old when compared with younger patients. Patients ≥65 years old had a higher incidence of discontinuation due to an adverse reaction (AR) and a higher incidence of serious ARs than younger patients.
The effect of end-stage renal disease (CLCR <15 mL/min) or hemodialysis on XPOVIO pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc. at 1-888-209-9326 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
© 2025 Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc.
X

